publications
2025
- arXiv
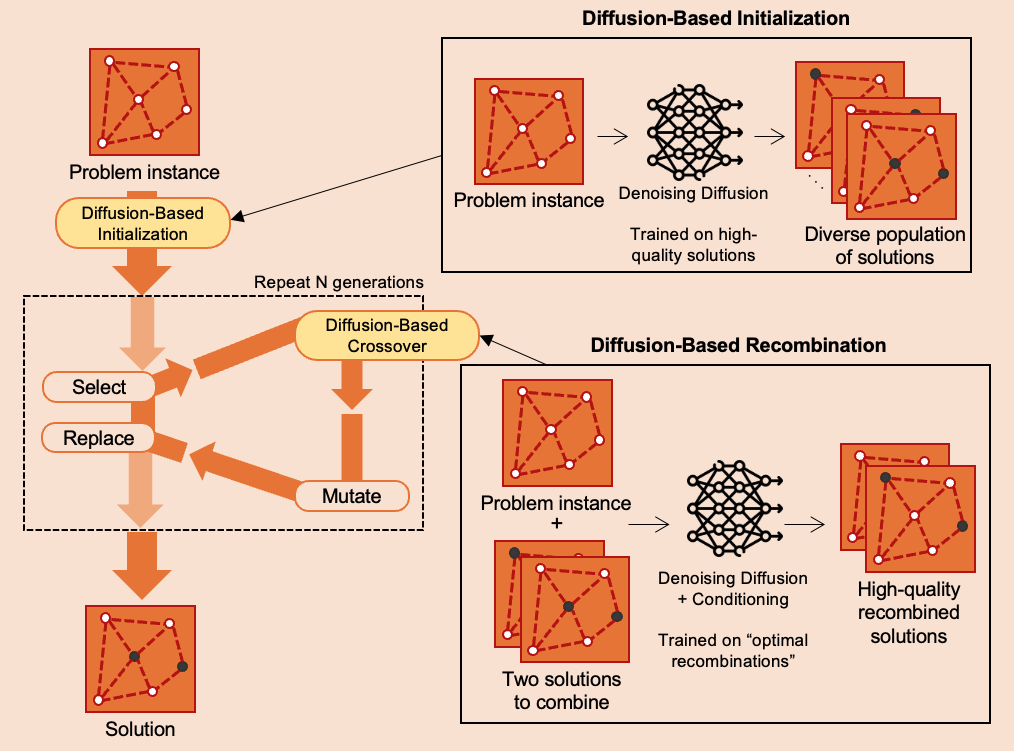 A Denoising Diffusion-Based Evolutionary Algorithm Framework: Application to the Maximum Independent Set ProblemJoan Salvà Soler and Günther R. RaidlarXiv preprint arXiv:2510.08627, 2025
A Denoising Diffusion-Based Evolutionary Algorithm Framework: Application to the Maximum Independent Set ProblemJoan Salvà Soler and Günther R. RaidlarXiv preprint arXiv:2510.08627, 2025Denoising diffusion models (DDMs) offer a promising generative approach for combinatorial optimization, yet they often lack the robust exploration capabilities of traditional metaheuristics like evolutionary algorithms (EAs). We propose a Denoising Diffusion-based Evolutionary Algorithm (DDEA) framework that synergistically integrates these paradigms. It utilizes pre-trained DDMs for both high-quality and diverse population initialization and a novel diffusion-based recombination operator, trained via imitation learning against an optimal demonstrator. Evaluating DDEA on the Maximum Independent Set problem on Erdős-Rényi graphs, we demonstrate notable improvements over DIFUSCO, a leading DDM solver. DDEA consistently outperforms it given the same time budget, and surpasses Gurobi on larger graphs under the same time limit, with DDEA’s solution sizes being 3.9% and 7.5% larger on the ER-300-400 and ER-700-800 datasets, respectively. In out-of-distribution experiments, DDEA provides solutions of 11.6% higher quality than DIFUSCO under the same time limit. Ablation studies confirm that both diffusion initialization and recombination are crucial. Our work highlights the potential of hybridizing DDMs and EAs, offering a promising direction for the development of powerful machine learning solvers for complex combinatorial optimization problems.
@article{salva2025diffusion, title = {A Denoising Diffusion-Based Evolutionary Algorithm Framework: Application to the Maximum Independent Set Problem}, author = {Salvà Soler, Joan and Raidl, Günther R.}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2510.08627}, year = {2025}, } - arXiv
 A Fast GRASP Metaheuristic for the Trigger Arc TSP with MIP-Based Construction and Multi-Neighborhood Local SearchJoan Salvà Soler and Grégoire LambertyearXiv preprint arXiv:2508.08477, 2025
A Fast GRASP Metaheuristic for the Trigger Arc TSP with MIP-Based Construction and Multi-Neighborhood Local SearchJoan Salvà Soler and Grégoire LambertyearXiv preprint arXiv:2508.08477, 2025The Trigger Arc Traveling Salesman Problem (TA-TSP) extends the classical TSP by introducing dynamic arc costs that change when specific "trigger" arcs are traversed, modeling scenarios such as warehouse operations with compactable storage systems. This paper introduces a GRASP-based metaheuristic that combines multiple construction heuristics with a multi-neighborhood local search. The construction phase uses mixed-integer programming (MIP) techniques to transform the TA-TSP into a sequence of tailored TSP instances, while the improvement phase applies 2-Opt, Swap, and Relocate operators. Computational experiments on MESS 2024 competition instances achieved average optimality gaps of 0.77% and 0.40% relative to the best-known solutions within a 60-second limit. On smaller, synthetically generated datasets, the method produced solutions 11.3% better than the Gurobi solver under the same time constraints. The algorithm finished in the top three at MESS 2024, demonstrating its suitability for real-time routing applications with state-dependent travel costs.
@article{salva2025grasp, title = {A Fast GRASP Metaheuristic for the Trigger Arc TSP with MIP-Based Construction and Multi-Neighborhood Local Search}, author = {Salvà Soler, Joan and de Lambertye, Grégoire}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2508.08477}, year = {2025}, } - Master’s Thesis
 Denoising Diffusion-Based Evolutionary Algorithms: Exploring Hybridizations of Evolutionary Algorithms with Denoising Diffusion ModelsJoan Salvà Soler2025
Denoising Diffusion-Based Evolutionary Algorithms: Exploring Hybridizations of Evolutionary Algorithms with Denoising Diffusion ModelsJoan Salvà Soler2025This thesis explores the integration of denoising diffusion models with evolutionary algorithms (EAs) to enhance machine learning-based combinatorial optimization. While diffusion models have shown promise as generative solvers for NP-hard problems, they often rely on problem-specific heuristics and lack the robust exploration capabilities of traditional search methods. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Diffusion-based Evolutionary Algorithm (DEA) framework. This approach leverages pre-trained diffusion models for both population initialization and recombination, effectively exploiting the multimodal solution space captured by diffusion models within the exploratory structure of an EA. We focus on the Maximum Independent Set (MIS) problem, developing a baseline EA and then introducing diffusion-based initialization and a diffusion recombination operator trained via imitation learning from an optimal recombination demonstrator formulated as an Integer Linear Program.Computational experiments on Erdős-Rényi graph datasets of varying sizes demonstrate that DEA significantly outperforms standalone Difusco, a state-of-the-art diffusion-based solver for combinatorial optimization, achieving improved solution quality and better out-of-distribution generalization to larger graph instances. Notably, DEA outperforms the MIP solver Gurobi on larger instances when considering the same time limit, while still falling short of highly specialized classical solvers like KaMIS.Our ablation studies highlight the crucial contributions of both diffusion-based initialization and recombination to the DEA framework’s success. This work provides empirical evidence for the synergistic potential of combining diffusion models and EAs, offering a promising direction for developing more robust and effective machine learning approaches to complex combinatorial optimization problems and paving the way for future research into hybrid ML-metaheuristic methods.
@thesis{salva2025diffusion-thesis, title = {Denoising Diffusion-Based Evolutionary Algorithms: Exploring Hybridizations of Evolutionary Algorithms with Denoising Diffusion Models}, author = {Salvà Soler, Joan}, school = {Technische Universität Wien}, year = {2025}, advisor = {Raidl, Günther R.}, organisational_unit = {E192 - Institut für Logic and Computation}, publisher = {reposiTUm}, type = {Diploma Thesis}, language = {English}, pages = {92}, doi = {10.34726/hss.2025.126686}, url = {https://doi.org/10.34726/hss.2025.126686}, handle = {http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12708/215616}, catalogplus = {AC17527191}, keywords = {Diffusion Models; Evolutionary Algorithms; Maximum Independent Set; Combinatorial Optimization; Neural Combinatorial Optimization; Mixed Integer Programming}, }
2024
- CEJOR
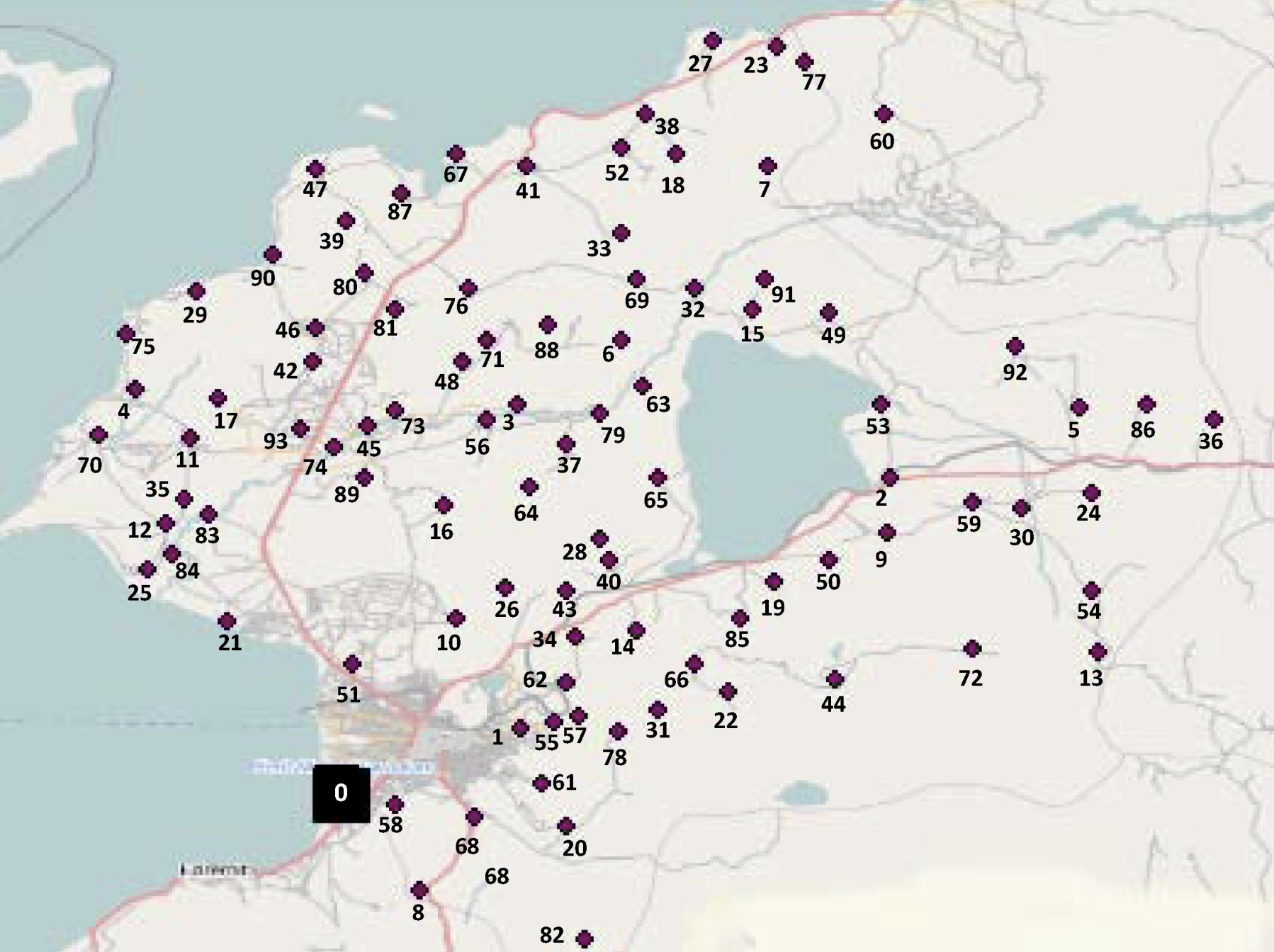 Exact methods for the Selective Assessment Routing ProblemJoan Salvà Soler, Vera C. Hemmelmayr, and Günther R. RaidlCentral European Journal of Operations Research, 2024
Exact methods for the Selective Assessment Routing ProblemJoan Salvà Soler, Vera C. Hemmelmayr, and Günther R. RaidlCentral European Journal of Operations Research, 2024The Selective Assessment Routing Problem (SARP) is a problem in humanitarian logistics addressing the site selection and routing decisions of rapid needs assessment teams which aim to evaluate the post-disaster conditions of different community groups, each carrying a distinct characteristic. The aim is to construct an assessment plan that maximizes the covering of different characteristics in a balanced way. We explore exact approaches based on mixed integer linear programming. Different mathematical formulations are presented, and theoretical results regarding their strengths are derived. The models are experimentally evaluated on a set of test instances including a real-world scenario.
@article{salva2024exact, title = {Exact methods for the Selective Assessment Routing Problem}, author = {Salvà Soler, Joan and Hemmelmayr, Vera C. and Raidl, Günther R.}, journal = {Central European Journal of Operations Research}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s10100-024-00943-y}, }